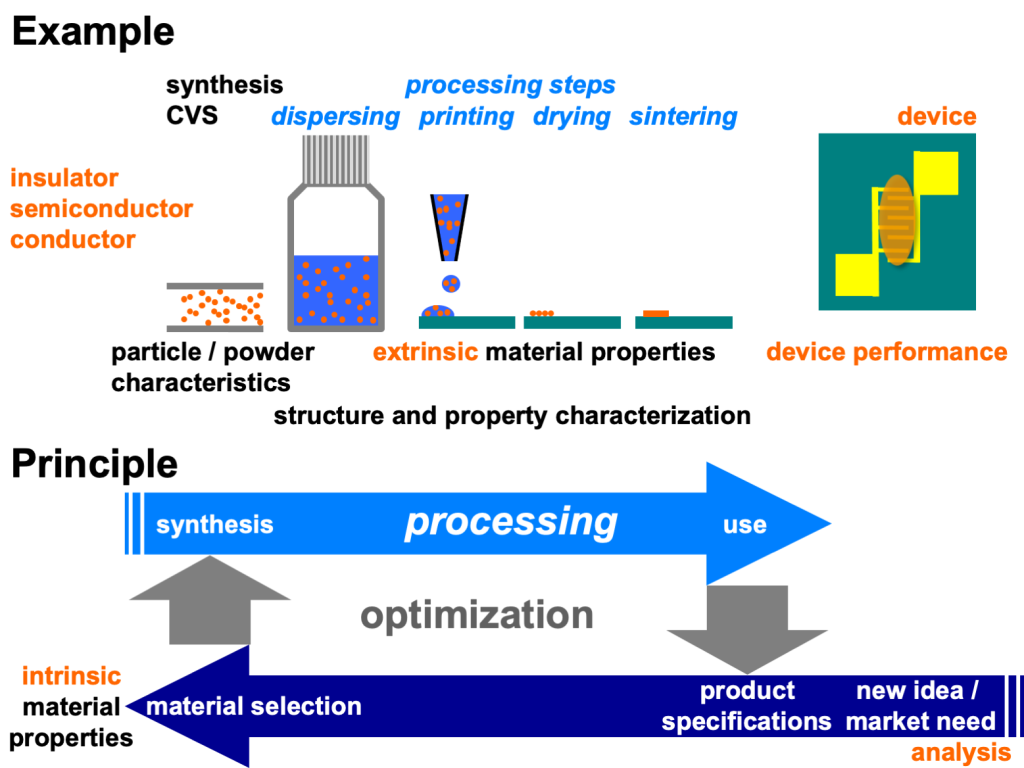
Materials properties and functionality in applications in form of parts or devices depend often on the processing of nanoparticles which also allows their integration into the micro- or macrospic world.
Influencing device performance already at the time of nanoparticle synthesis is a big challenge since product design and materials synthesis are so far apart. According to Ashby, product design starts with analysis of a new idea or market need, for example printed electronics. This analysis provides product specifications from which we can derive required materials properties. The corresponding materials selection determines then the intrinsic materials properties which can be modified during synthesis and processing along the process chain.
We use methods of colloid processing and powder technology to modify and process nanoparticles and nanomaterials.
Colloidal processing: Functionalization and Dispersion
Starting from nanoparticles generated by CVS in form of powders we need process them to obtain stable colloidal dispersions. This is especially challenging for small nanoparticles. We use ultrasonic agitation as comminution process to deagglomerate the nanoparticles. Surface chemistry needs to be controlled for example by variation of the zeta-potential through pH adjustment or by chemisorption of ligands either already in the gas phase synthesis or in the colloidal state.
Particle Deposition
Particle deposition may be performed by printing which allows the placement of particles on specific locations on a substrate. We use ink jet printing. Inks are colloids optimized regarding particle size, colloidal stability, viscosity, and surface energy to obtain high printability.
Powder Technology: Compaction and Sintering
In case of (dry) nanoscaled powders the goal and challenge is typically to obtain dense nanoscaled polycrystalline materials. Compaction, typically via uniaxial pressing and sintering, conventionally in a furnace or by laser or current sintering, are processes to convert nanoscaled powders into nanocrystalline solids.
- C. Gorynski, J. Geiß, U. Anselmi-Tamburini, and M. Winterer, Structural and compositional gradients in alternating current sintered aluminum-doped zinc oxide, Acta Materialia 270 (2024) 119855
- V. Mackert, T. Winter, S. Jackson, R. Kalia, A. Levish, S. Lukic, J. Geiss, and M. Winterer, Very Small Nanocrystalline Tin Dioxide Particles: Local-, Crystal-, and Micro-Structure, J. Phys. Chem. C 127 (2023) 17389-17405
- C. Gorynski, M. Frei, F. E. Kruis, M. Winterer, Machine learning based quantitative characterization of microstructures, Acta Mater. 256 (2023) 119106, 17pp.
- A. Levish and M. Winterer, Formation of polymorphs and pores in small nanocrystalline iron oxide particles, Sci. Rep. 12 (2022) 15291, 11pp
- V. Mackert, M. A. Schroer, M. Winterer, Unraveling agglomeration and deagglomeration in aqueous colloidal dispersions of very small tin dioxide nanoparticles, J. Colloid and Interface Science 608 (2022) 2681?2693
- C. Gorynski , U. Anselmi-Tamburini, and M. Winterer, Controlling current flow in sintering: A facile method coupling flash with spark plasma sintering, Rev. Sci. Instr. 91 (2020), 015112, 10pp
- V. Mackert, J. S. Gebauer, C. Notthoff, and M. Winterer, Zinc stannate by reactive laser sintering, Appl. Surf. Sci. 457 (2018), 1174-1180
- J. S. Gebauer, V. Mackert, S. Ognjanovic, M. Winterer, Tailoring metal oxide nanoparticle dispersions for inkjet printing, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 526 (2018), 400-409
- S. K. Garlapati, G. C. Marques, J. S. Gebauer, S. Dehm, M. Bruns, M. Winterer, M. B. Tahoori, J. Aghassi-Hagmann, H. Hahn, and S. Dasgupta, High performance printed oxide field-effect transistors processed using photonic curing, Nanotechnology 29 (2018) 235205
- S. K. Garlapati, J. S. Gebauer, S. Dehm, M. Bruns, M. Winterer, H. Hahn, and S. Dasgupta, Room-Temperature Processing of printed Oxide FETs Using Ultraviolet Photonic Curing, Adv. Electron. Mater, 3 (2017), 1600476
- A. Sandmann, A. Kompch, V. Mackert, Chr. Liebscher, M. Winterer, Interaction of L-Cysteine with ZnO: Structure, Surface Chemistry, and Optical Properties, Langmuir 31 (2015), 5701-5711
- D. Gautam, M. Engenhorst, C. Schilling, G. Schierning, R. Schmechel, and M. Winterer, Thermoelectric properties of pulsed current sintered nanocrystalline Al-doped ZnO by chemical vapour synthesis, J. Mat. Chem. A 3 (2015), 189
- Y. L. Gao, V. V. Shvartsman, D. Gautam, M. Winterer, and D. C. Lupascu, Nanocrystalline Barium Strontium Titanate Ceramics Synthesized via the ?Organosol? Route and Spark Plasma Sintering, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 97 (2014), 2139-2146
- A. Wittmar, D. Gautam, C. Schilling, U. Dorfler, W. Mayer-Zaika, M. Winterer, and M. Ulbricht, Stable zinc oxide nanoparticle dispersions in ionic liquids, J. Nanopart. Res. 16 (2014), 2341
- K. Maca, M. Kachlik, P. Vanek, Gautam, and M. Winterer, The influence of sintering conditions on the phase purity of bulk EuTiO3 and Eu0.5Ba0.5TiO3 ceramics, Phase Trans. 86 (2013), 737-747
- A. Wittmar, M. Gajda, D. Gautam, U. Dorfler, M. Winterer, and M. Ulbricht, Influence of the cation alkyl chain length of imidazolium-based room temperature ionic liquids on the dispersibility of TiO2 nanopowders, Journal of Nanoparticle Research 15/3 (2013), 1463
- A. Sandmann, C. Notthoff, and M. Winterer, Continuous wave ultraviolet-laser sintering of ZnO and TiO2 nanoparticle thin films at low laser powers, Journal of Applied Physics 113/4 (2013), 044310
- A. S. G. Khalil, S. Hartner, M. Ali, H. Wiggers, and M. Winterer, Stable Aqueous Dispersions of ZnO Nanoparticles for Ink-Jet Printed Gas Sensors, Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology 11 (2011), 10839-10843
- A. Gupta, A.S.G. Khalil, M. Offer, M. Geller, M. Winterer, A. Lorke, and H. Wiggers, Synthesis and Ink-Jet Printing of Highly Luminescing Silicon Nanoparticles for Printable Electronics, Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology 11 (2011), 5028-5033
- V. V. Srdic and M. Winterer, Comparison of nanosized zirconia synthesized by gas and liquid phase methods, J. Europ. Ceram. Soc. 26 (2006), 3145-3151
- K. K. Akurati, S. S. Bhattacharya, M. Winterer, and H. Hahn, Synthesis, characterization and sintering of nanocrystalline titania powders produced by chemical vapour synthesis, J. Phys. D-Appl. Phys. 39 (2006), 2248-2254
- V. V. Srdic, M. Winterer, and H. Hahn, Nanocrystalline Zirconia Surface Doped with Alumina: Chemical Vapor Synthesis, Characterization and Properties, J. Am. Ceramic Soc. 84 (2001), 2771
- V. V. Srdic, M. Winterer, and H. Hahn, Sintering Behavior of Nanocrystalline Zirconia Doped with Alumina Prepared by Chemical Vapor Synthesis, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 83 (2000), 1853
- V. V. Srdic, M. Winterer, G. Miehe and H. Hahn, Different Zirconia-Alumina Nanopowders by Modifications of Chemical Vapor Synthesis, Nanostructured Materials 12 (1999), 95
- V. V. Srdic, M. Winterer, and H. Hahn, Sintering Behavior of Nanocrystalline Zirconia Prepared by Chemical Vapor Synthesis, J. Am. Ceramic Soc. 83 (2000), 729